Step by Step FastAPI Setup
Set up FastAPI to build high-performance APIs with Python, featuring automatic docs, async support, and easy integration.
This guide shows the step-by-step setup of FastAPI on Windows OS and VS Code IDE.
-
Navigate to Download Python, download and install Python with admin privileges and add python.exe to the PATH.
-
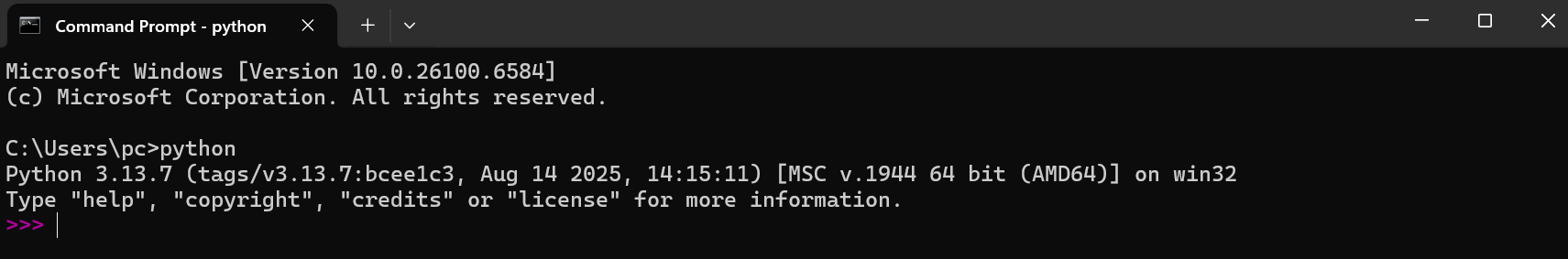
Verify that Python is successfully installed by running the Python command in CMD:
-
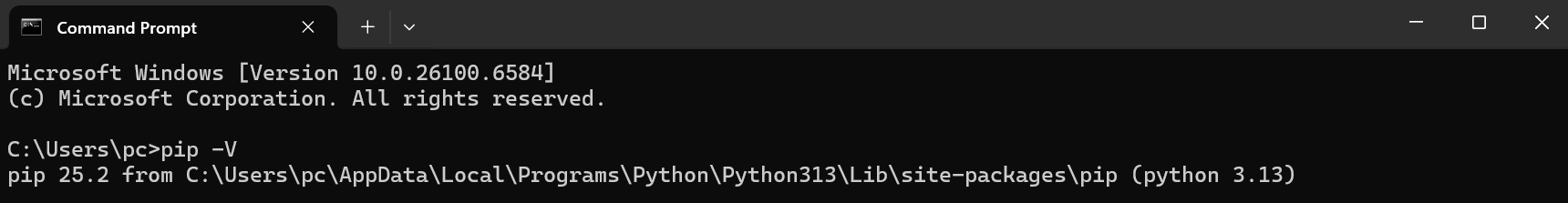
Verify that PIP (Python package installer) is installed by running the command in CMD:
- Create a project directory folder(ex. fastapi-setup in a folder named Code on drive D).
1 2
D:\cd Code D:\Code> mkdir fastapi-setup
- From now on, let’s use VS Code to perform other FastAPI setup steps. Open a previously created folder in VS Code and run terminal from Terminal > New Terminal. We need to create a virtual environment inside our project by running the following command:
1
python -m venv .venvIf Python not found message appears, restart your PC to update Python installation PATH variables.
python -m venv .venv command creates a new virtual environment in a directory called .venv.
- Activate the Virtual Environment
1
.venv\Scripts\Activate.ps1
If previous command doesn’t activate the virtual environment and there is an error message: Activate.ps1 : The term ‘Activate.ps1’ is not recognized as the name of a cmdlet, function, script file, or operable program. Check the spelling of the name, or if a path was included, verify that the path is correct and try again. If you trust this command, instead type: “.\activate”. See “get-help about_Command_Precedence” for more details. then:
- Step 1: run the command:
Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned -Scope CurrentUser- Step 2: run the command to activate virtual environment
- Check the Virtual Environment is active
1
Get-Command python
If it shows the python binary at .venv\Scripts\python, inside of your project (in this case fastapi-setup), then it worked.

- Run the following command to install FastAPI
1 2
# Make sure you put "fastapi[standard]" in quotes to ensure it works in all terminals. pip install "fastapi[standard]"
- Create main.py inside project and add following code to test and run FastAPI server
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
from typing import Union
from fastapi import FastAPI
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/")
def read_root():
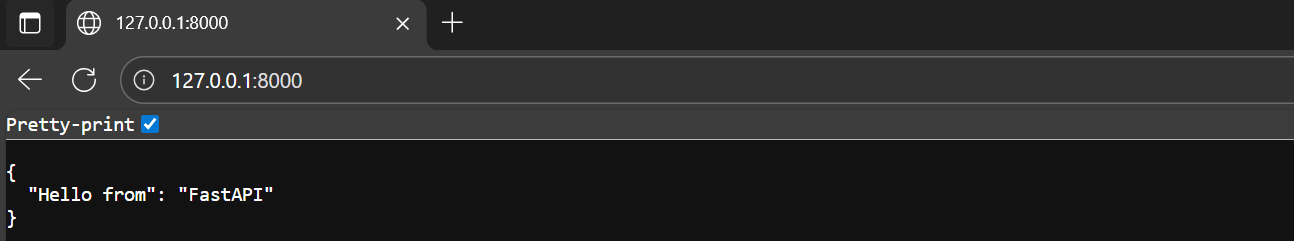
return {"Hello from":"FastAPI"}
- Run FastAPI server with:
1
fastapi dev main.py
- Go to 127.0.0.1:8000. If setup was done properly than response should be displayed similar to image below.
- Deactivate virtual environment
1 2
# In .venv folder .\deactivate
Key Takeaways
- Create a project and open folder in VS Code.
- Create a virtual environment:
1
uv venv
- Activate virtual environment and do this every time you start a new terminal session to work on the project.
1
.venv\Scripts\Activate.ps1
-
Every time you install a new package in that environment, activate the environment again.
- Check the Virtual Environment is Active
1
Get-Command python
If it shows the python binary at .venv\Scripts\python, inside of created project, then it worked.
- Install packages - after activating the environment, you can install packages in it.
1
pip install "fastapi[standard]"
-
Create main.py and write some code.
- Run the FastAPI server.
1
fastapi dev main.py
- Deactivate the virtual environment.
1
deactivate
- Activate virtual environment again when starting working on a project.