Technology Roadmap - The Need And Roadmap Types
Explore what a technology roadmap is, its purpose, and types like product, IT, and infrastructure roadmaps for strategic tech planning.
A technology roadmap is a high-level, visual plan that communicates an organization’s technology strategy. It is also known as an IT roadmap and it helps internal teams make strategic decisions around their technology infrastructure. There are several kinds of technology roadmaps:
- Enterprise IT roadmap
- IT/Cloud Infrastructure roadmap
- Architecture/Software Engineering roadmap
- CyberSecurity roadmap
- Internal IT/Systems roadmap
- IT Assets Procurement roadmap
Enterprise IT Roadmap
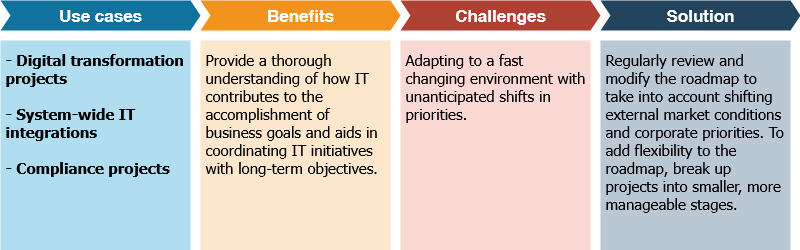
This high-level roadmap illustrate the organization’s full information technology architecture, including programs such as digital transformation, change management, enterprise service management, and legal compliance.
Developing Enterprise roadmap is a beneficial early-stage planning exercise for an enterprise architect or other IT professional tasked with handling a major IT initiative because it helps organization to prioritize the numerous actions, focus and clarify strategic thinking, and gain support and approval from key stakeholders.
IT/Cloud Infrastructure Roadmap
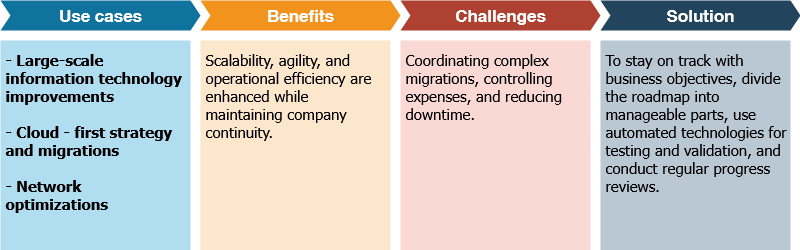
This roadmap lays out a strategic plan for improving an organization’s IT infrastructure, with a focus on critical areas including cloud migrations, server upgrades, and network developments.
Platform Engineering roadmaps belongs to strategic IT/Cloud Infrastructure roadmap with a goal of strategic plans for improving DevOps techniques within an organization. It covers important topics including infrastructure automation, tooling advancements, and CI/CD improvements. This strategy guarantees that DevOps projects improve operational effectiveness, stay in line with company goals, and uphold a robust level of security.
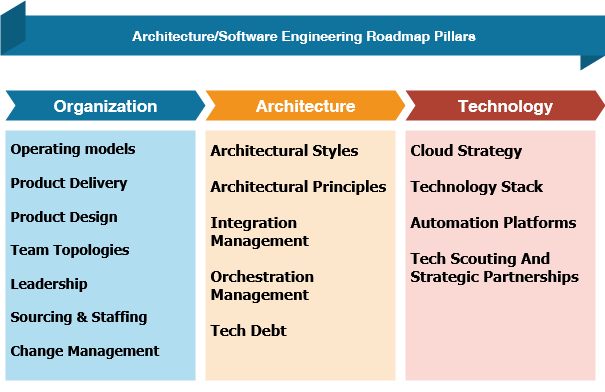
Architecture/Software Engineering Roadmap
Architecture roadmap describes a strategy for updating and improving an organization’s system architecture. It focuses scalability enhancements, microservices adoption, and system architectural modifications. This roadmap ensures that architectural efforts enhance system performance while keeping scalability and stability as top priorities. A strategy plan for developing and improving a software product is laid out in software roadmap, with a focus on platform improvements, bug fixes and feature releases. It also guarantees that software development efforts are in line with user requirements.
The foundational pillars of architecture and software engineering roadmap fall under:
- Organization
- Architecture
- Technology
The Operating model is about establishing and fulfilling activities related to the organization’s business. It covers operational day-to-day activities such as people and process management. The main components of an operating model are:
- Guiding principles - often linked to strategic objectives and focus.
- Organizational structure - covers the layout and structure of the organization.
- Processes - outlines how work is conducted with other components like people, tools and department specific activities.
- Technology - includes layers of technology such as physical infrastructure, software tools and data.
- People - this covers talent aquisitions and retention, responsabilities, leadership and management
- Culture - values, behaviors, vision and other factors that influence how and why work is conducted.
CyberSecurity Roadmap
A security roadmap derives directly from the process of creating an annual cybersecurity program strategy. Formulating a cybersecurity vision based on practical business, technological, and economic factors is the first step in that strategic planning process. To address potential risks and vulnerabilities and build a successful cyber security policy, an organization must have an up-to-date architecture that includes system assets, communication links, and connections to external systems. Identifying what needs to be safeguarded may be done by understanding the boundaries of the system and the assets that fall within it. A few benefits of creating an effective cybersecurity roadmap are:
- A clear and systematic plan for addressing cybersecurity risks and vulnerabilities.
- Improved coordination between corporate goals and cybersecurity activities.
- Better communication and collaboration between cybersecurity teams and stakeholders.
- More effective budgeting and resource allocation for cybersecurity initiatives.
- Early detection and prevention of possible cyberthreats.
The main steps for creating an Cybersecurity roadmap are:
- Cybersecurity assessment - should focus on application security, identity and access management, data protection and incident response.
- Set objectives and goals - targeted maturity level and SMART goals.
- Action plan development - detailed actions for applying new security controls, updating exisiting security procedures, employees training on cybersecurity best practices.
- Communication - with key stakeholders and cross department collaboration.
- Reviews and regular cybersecurity assessments.
Internal IT/Systems Roadmap
Internal IT roadmap presents a strategy plan for a company’s IT department, with a focus on essential areas including infrastructure upgrades, system integrations, and cybersecurity projects. This systematic strategy guarantees that IT initiatives are in line with company objectives, mitigate risks, improve overall security and efficiency. A few examples components of this roadmap include:
- Working machines and servers upgrades.
- Implementing storage solutions.
- Expand and improve network bandwidth.
- SSO and multi-factor implementation accross platforms.
- Support cybersecurity best practices implementation.
IT Assets Procurement Roadmap
IT procurement (also known as Information Technology procurement) is the process by which businesses acquire IT assets. The true value of any IT procurement process is ensuring that each purchase (and thus every IT asset) is aligned with the organization’s strategy, goals, budget, and future plans. Purchasing IT is crucial since it impacts how business runs, expands, and maintains security. The key functions of this roadmap include:
- Detailed information on the hardware and software tools needed, taking into account long-term planning and cost-effectiveness.
- A plan for strategic sourcing: The activities of discovering, assessing, and selecting suppliers to ensure that the company receives the best value for money.
- Negotiation Activities and Contract Management: This includes negotiating terms and conditions with suppliers as well as contract management to assure compliance and optimal performance.
- Supplier Relationship Management (SRM) - focuses on developing actions steps for maintaining positive relationships with suppliers in order to promote collaboration, address concerns quickly, and drive continuous improvement.